With Symbiotic's mainnet launch, network builders can now access economic security, while stakers can participate across multiple networks through a single deposit. This is made possible through Symbiotic vaults - smart contracts that coordinate capital between stakers, operators, and networks.
Vaults represent a fundamental shift in how blockchain networks manage security. Traditional systems require networks to bootstrap and maintain isolated staking pools, fragmenting capital and limiting participation. Symbiotic vaults break down these silos, creating an efficient marketplace where networks tap into a shared pool of collateral, stakers maximize their capital efficiency, and node operators manage their participation in multiple protocols simultaneously.
How Vaults Work
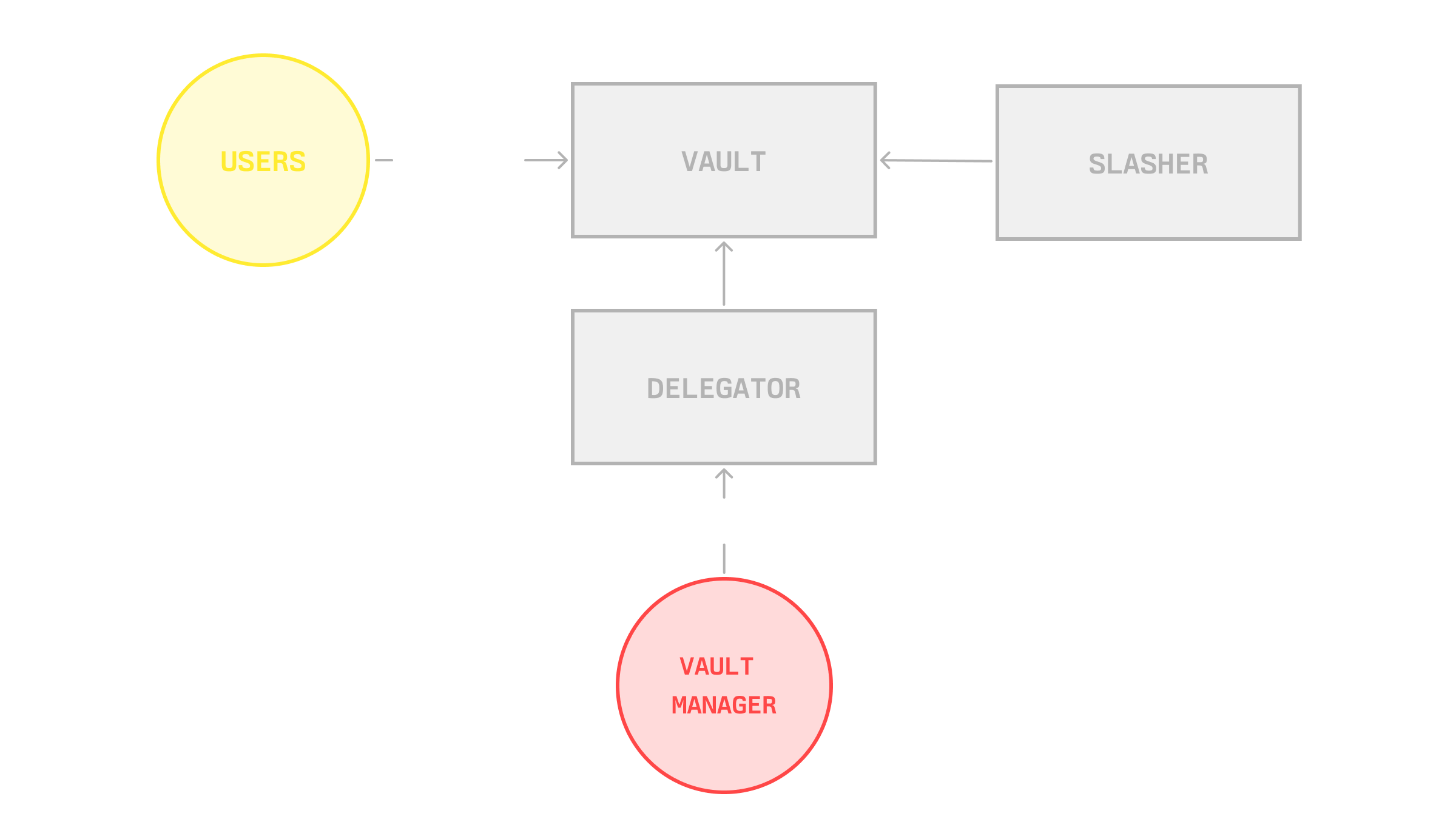
At their core, Symbiotic vaults coordinate economic security through three specialized modules. The Accounting Module manages deposits and withdrawals, tracking each participant's share. The Slashing Module enforces penalties for misbehavior according to each network's rules. The Delegation Module determines how capital flows to networks and operators, implementing differentiated strategies to balance efficiency and risk.
Delegatable vaults come in two main varieties: public and private. Public vaults allow for any staker to deposit assets directly from the Symbiotic interface. Private vaults are managed through a third-party interface (LRTs, operators, institutions) and can be interacted with on their respective websites.
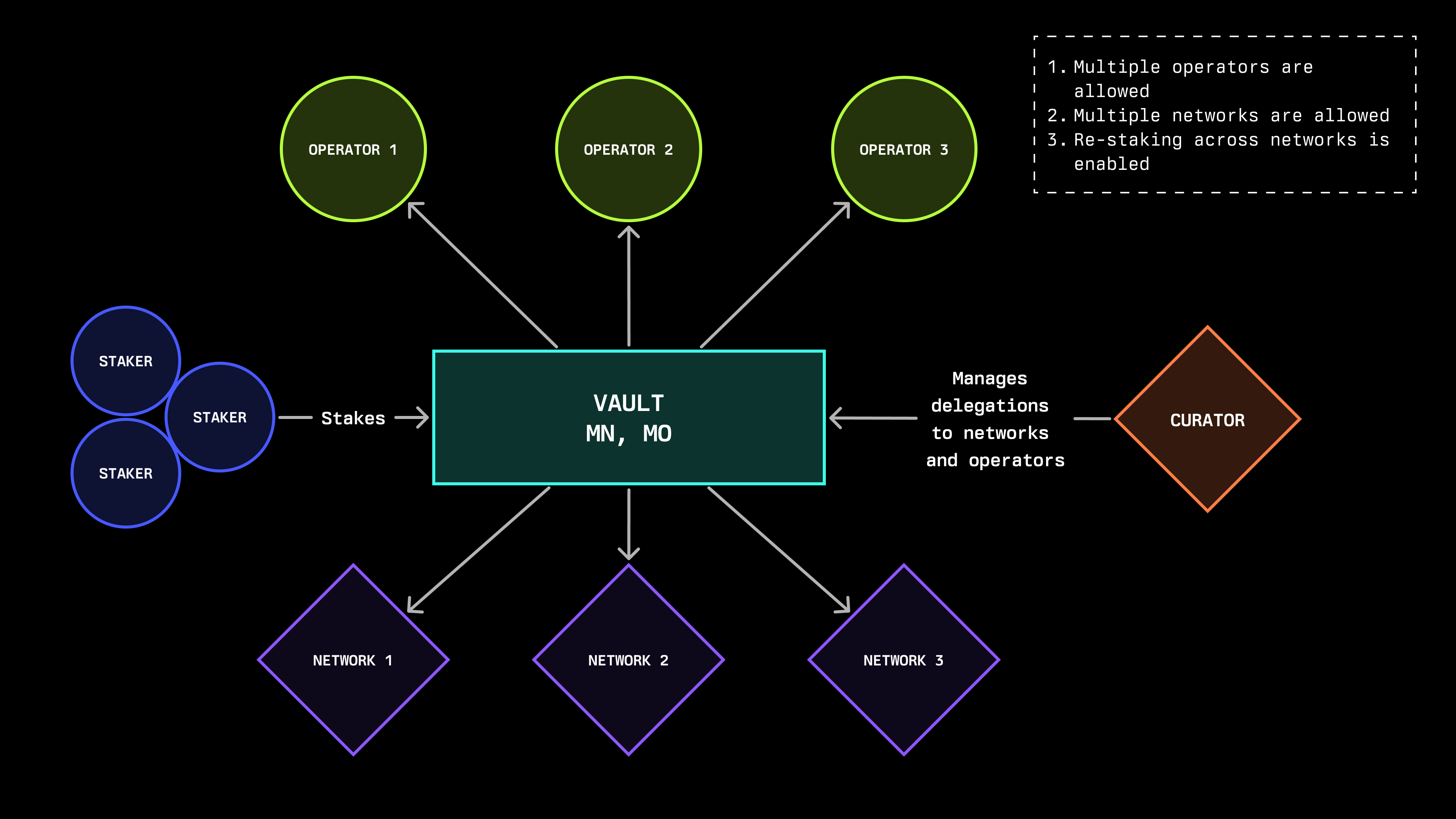
A vault’s delegation strategy significantly impacts network decentralization. Restaking across multiple networks maximizes capital efficiency but introduces shared risk between networks - if one network experiences issues, it could affect others. More isolated strategies improve security boundaries but reduce capital efficiency. Each network must explicitly accept a vault's restaking configuration and security model before receiving stake. Operator performance within each strategy affects decentralization through their geographic distribution, infrastructure diversity, and reliability. For more information regarding the types of delegation strategies, refer to our documentation: https://docs.symbiotic.fi/modules/vault/delegator
Considerations for Stakers
There are two major types of vaults: pre-deposit and actively delegated vaults. Pre-deposit vaults are transitory and designed to preallocate required stake before active delegation.
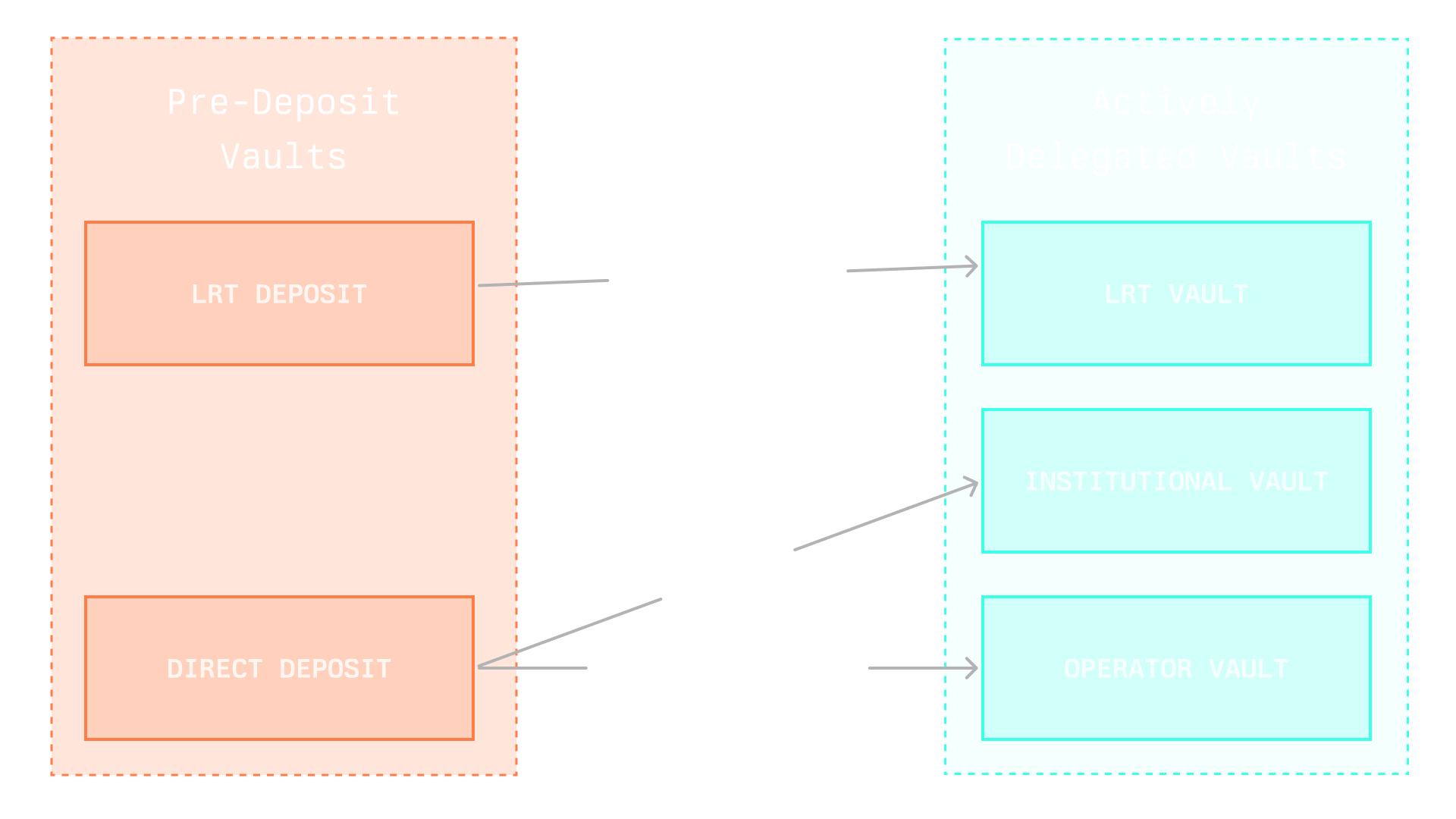
With the launch of actively delegated vaults, migration is an option, but there is no deadline to migrate, and you will still earn points in predeposit vaults. The LRT provider will handle migration for you if your assets are deposited from an LRT. For more information regarding points, please refer to our documentation: https://docs.symbiotic.fi/points-season2
The security model of each vault plays a crucial role in risk management. Some vaults implement resolver systems where designated entities (network DAOs, security councils, or multisig committees) can veto invalid slashing attempts within a specified timeframe. Before receiving stake, networks must explicitly accept these security configurations, including resolver identities and veto timeframes.
Withdrawal delays represent another key feature in vault design that ensures proper staking conditions, with a single vault capable of simultaneously supporting an extensive list of networks.
Before depositing, users should understand their vault's current network delegations and how the vault's epoch duration affects the withdrawal timeline, as withdrawing stake will take between one and up to two full vault epochs (learn more about withdrawals here).
Looking Forward
The launch of Symbiotic vaults marks a crucial step toward efficient shared security coordination. While initial implementations focus on core functionality, the modular design enables future expansion into more sophisticated delegation strategies and security mechanisms. Support for assets from other blockchains becomes possible through collateral abstraction, further broadening participation options.
For technical specifications about vault mechanics, restaking configurations, and security models, visit our documentation. To explore our growing ecosystem of vault providers or learn more about integration possibilities, reach out to us here.